Communication #
Request-Response #
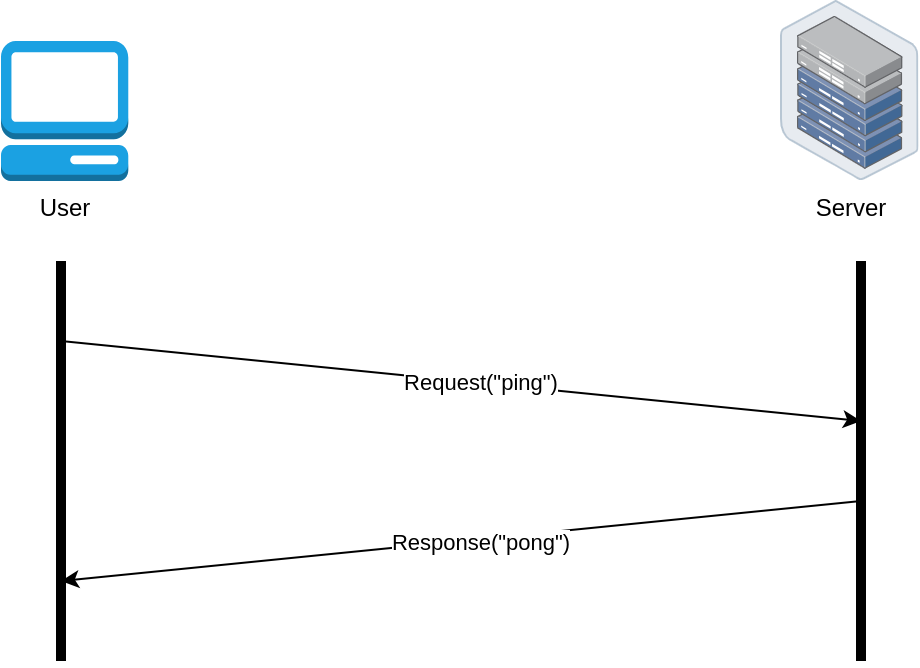
Overview #
- Fundamental communication pattern
- The most common patterns for communication in client-server architectures
Demo #
Server code
// server.js
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log(`Received request: ${req.method} ${req.url}`);
if (req.url === '/hello') {
if (req.method === 'POST') {
let body = '';
req.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk.toString(); // Convert buffer to string
});
req.on('end', () => {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
if (body.trim() === "ping") {
res.end('pong');
} else {
res.end('');
}
});
} else {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('world');
}
} else {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Not Found');
}
});
server.listen(2000, () => {
console.log('Server is listening on port 2000');
});
Client code
fetch('http://localhost:2000/hello', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' },
body: 'ping'
})
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => console.log(data)) // Should log: "pong"
Instruction
- Start the server by running
node server.js
1.1. Your terminal will display:Server is listening on port 2000 - Open your browser and enter:
http://localhost:2000/hello
2.1. Your terminal will first log:Received request: GET /hello
2.2. Then, your browser will display:world - Open the browser console and run Client code
3.1. Your terminal will first log:Received request: POST /hello
3.2. Then, your browser console will display:pong
Short Polling #
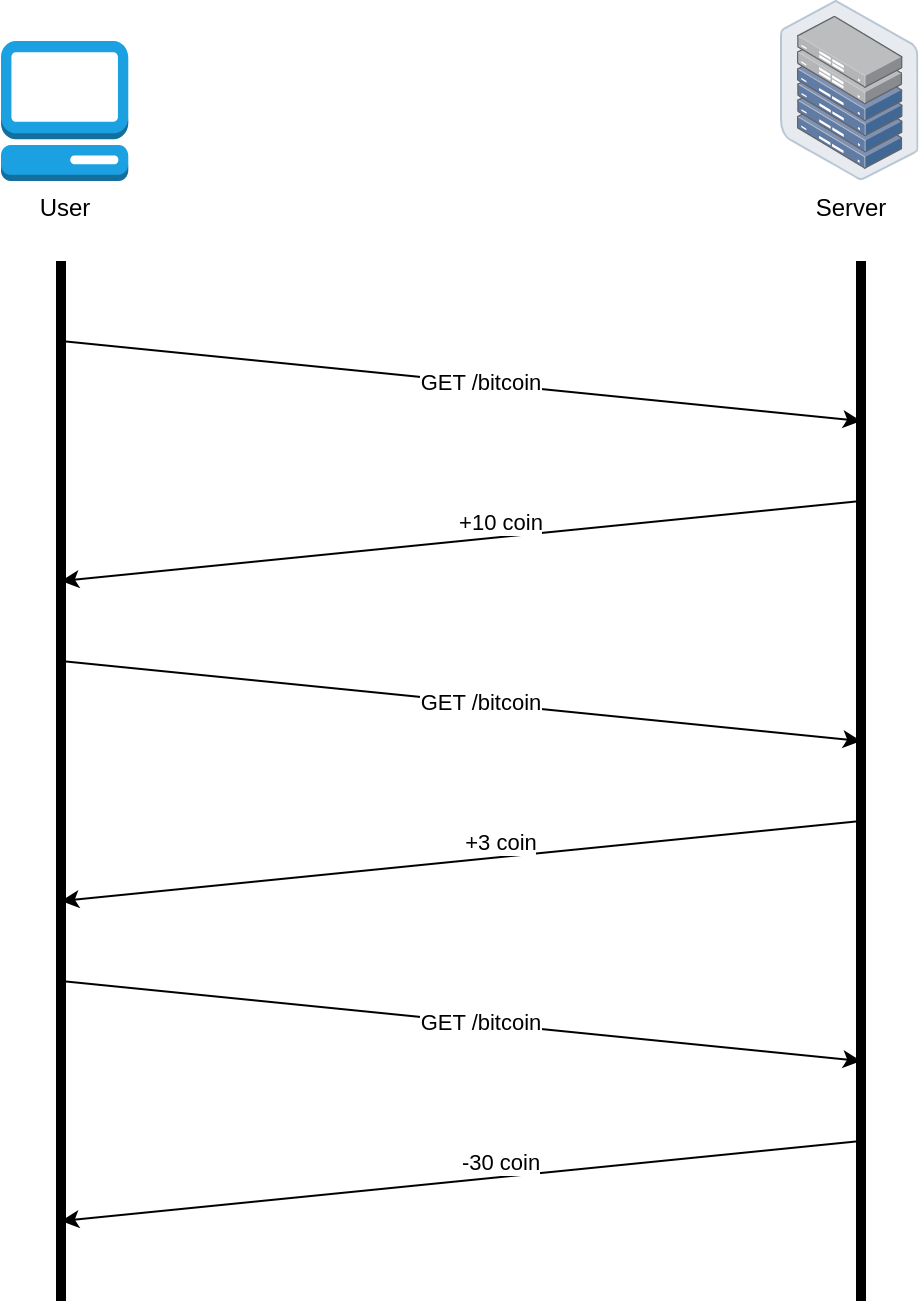
Overview #
- Based on the Request-Response design pattern
- Continuously polls the server for new updates
- Near real-time updates
- Client controls the frequency
Use case #
- Monitor stocks or cryptocurrencies
- Fetch status updates
- User notifications
Demo #
Server code
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 2000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello world');
});
app.get('/bitcoin', (req, res) => {
const randomValue = Math.floor(Math.random() * 111) - 10; // Random value between -10 and +100
res.json({ coins: randomValue });
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Client code
function fetchBitcoinData() {
fetch('http://localhost:2000/bitcoin')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(`Bitcoin value: ${data.coins}`);
});
}
setInterval(fetchBitcoinData, 1000);
Instruction
- Start the server by running
node server.js
1.1. Your terminal will display:Server is running at http://localhost:2000 - Open your browser and enter:
http://localhost:2000
2.1. Your browser will display:Hello world - Open the browser console and run Client code
3.1. Your browser console will continuously display:>> Bitcoin value: 10 >> Bitcoin value: 100 >> Bitcoin value: 26 >> Bitcoin value: -6 >> Bitcoin value: 65 ...
Long Polling #
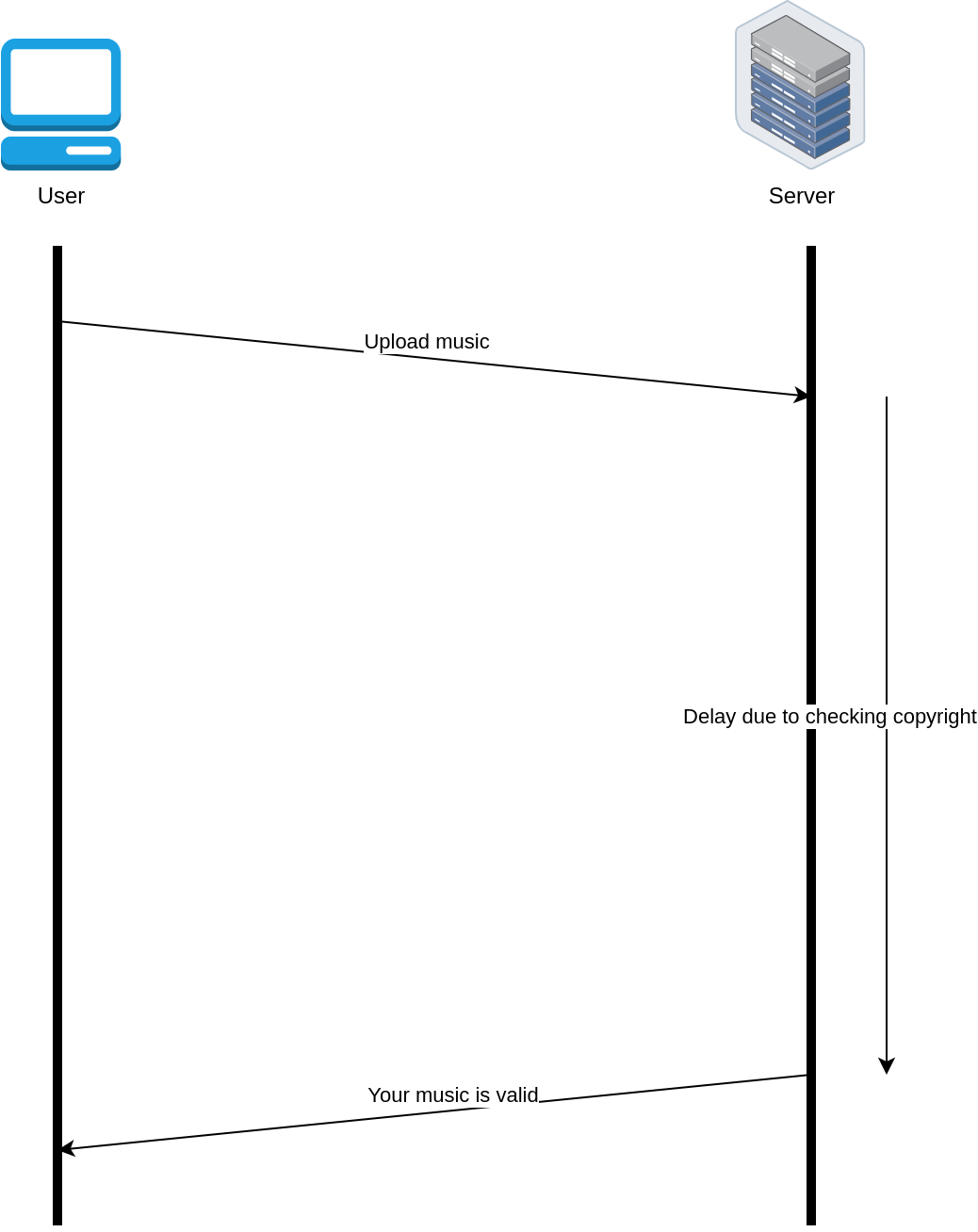
Overview #
- Based on the Request-Response design pattern
- Holds the request open and only responds after completing the task
- Real-time updates
- Server controls the timing of response
Use case #
- Fetch status updates
- User notifications
Demo #
Server code
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 2000;
app.use(express.json());
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello world');
});
app.post('/validate-music', (req, res) => {
const { musicName, capacity } = req.body;
// Simulate processing time with a random delay between 5 to 10 seconds
const delay = Math.floor(Math.random() * 6) + 5;
console.log(`Received request to validate music: ${musicName}, capacity: ${capacity}`);
setTimeout(() => {
res.json({ message: `The music "${musicName}" is valid.` });
}, delay * 1000);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Client code
function validateMusic(musicName, capacity) {
fetch('http://localhost:2000/validate-music', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ musicName, capacity })
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data.message);
});
}
validateMusic('Supernova', '5MB');
Instruction
- Start the server by running
node server.js
1.1. Your terminal will display:Server is running at http://localhost:2000 - Open your browser and enter:
http://localhost:2000
2.1. Your browser will display:Hello world - Open the browser console and run Client code
3.1. Your terminal will first log:Received request to validate music: Supernova, capacity: 5MB
3.2. Then, your browser console after some seconds will display:The music "Supernova" is valid.
Push #
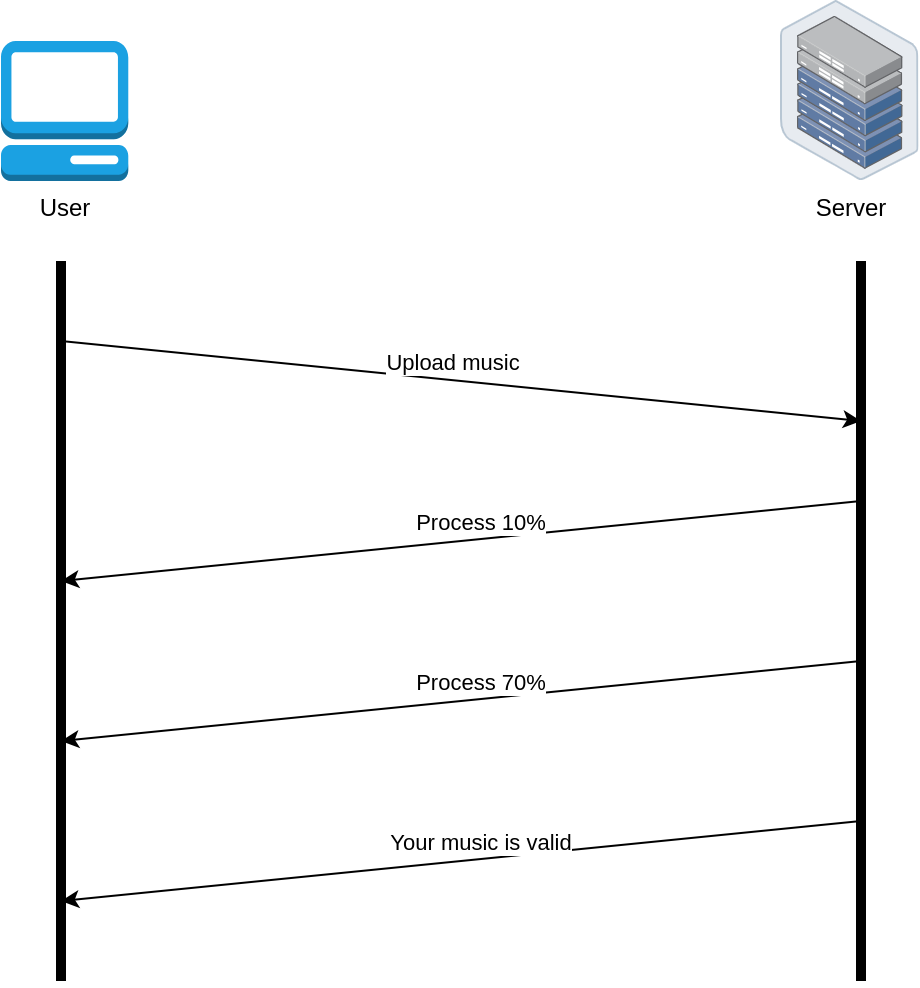
Overview #
- Real-time updates
Use case #
- Chat and messaging apps
- Notification systems
Demo Websocket #
- Bidirectional communication
Server code
// server.js
const http = require('http');
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const port = 2000;
// Create an HTTP server
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.url === '/') {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Hello, World!');
} else {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Not Found');
}
});
// Create a WebSocket server on top of the HTTP server
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ server });
wss.on('connection', ws => {
console.log('Client connected the WebSocket connection');
ws.on('message', message => {
console.log(`Received: ${message}`);
// Simulating music validation process
let progress = 0;
const interval = setInterval(() => {
progress += Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 10; // Random progress between 10% - 20%
if (progress >= 100) {
progress = 100;
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ status: 'complete', message: 'Music validation complete and valid!' }));
clearInterval(interval);
} else {
ws.send(JSON.stringify({ status: 'in-progress', progress: progress }));
}
}, 1000);
});
ws.on('close', () => {
console.log('Client disconnected the WebSocket connection');
});
});
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${port}`);
console.log(`WebSocket server running on ws://localhost:${port}`);
});
Client code
const socket = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:2000');
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (data.status === 'in-progress') {
console.log(`Validation progress: ${data.progress}%`);
} else if (data.status === 'complete') {
console.log(data.message);
socket.close();
}
};
socket.onopen = function() {
console.log('Connected to the server');
// Simulating a music upload with a title and arbitrary size
const musicData = {
title: 'My Awesome Track',
size: 1234
};
socket.send(JSON.stringify(musicData));
};
socket.onclose = function() {
console.log('Disconnected the WebSocket connection from the server');
};
Instruction
- Start the server by running
node server.js
1.1. Your terminal will display:Server running on http://localhost:2000 WebSocket server running on ws://localhost:2000 - Open your browser and enter:
http://localhost:2000
2.1. Your browser will display:Hello world - Open the browser console and run Client code
3.1. Your terminal will first log:3.2. Then, your browser console will display:Client connected the WebSocket connection Received: {"title":"My Awesome Track","size":1234}>> Connected to the server >> Validation progress: 18% >> Validation progress: 28% >> Validation progress: 39% >> Validation progress: 50% >> Validation progress: 65% >> Validation progress: 80% >> Validation progress: 97% >> Music validation complete and valid! >> Disconnected the WebSocket connection from the server
Demo Server-sent events #
- Unidirectional communication
Server code
// server.js
const http = require('http');
const port = 2000;
let currentProgress = 0;
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method === 'GET' && req.url === '/') {
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Hello, World!');
} else if (req.method === 'POST' && req.url === '/upload') {
let body = '';
req.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end', () => {
console.log('Received music data:', body);
currentProgress = 0;
let interval = setInterval(() => {
currentProgress += Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 10; // Random progress between 10% - 20%
if (currentProgress >= 100) {
currentProgress = 100;
clearInterval(interval);
}
}, 1000);
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Music data received and processing started');
});
} else if (req.method === 'GET' && req.url === '/uploadprogress') {
// Set headers for SSE
res.writeHead(200, {
'Content-Type': 'text/event-stream',
'Cache-Control': 'no-cache',
'Connection': 'keep-alive'
});
let interval = null;
const sendProgress = () => {
if (currentProgress < 100) {
res.write(`data: ${JSON.stringify({ status: 'in-progress', progress: currentProgress })}\n\n`);
} else {
res.write(`data: ${JSON.stringify({ status: 'complete', message: 'Music validation complete and valid!' })}\n\n`);
clearInterval(interval);
res.end();
}
};
interval = setInterval(sendProgress, 1000);
} else {
res.writeHead(404, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' });
res.end('Not Found');
}
});
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Client code
function uploadMusicData() {
const musicData = {
title: 'My Awesome Track',
size: 1234
};
fetch('http://localhost:2000/upload', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(musicData)
})
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
// Create an EventSource connection to the server
const eventSource = new EventSource('http://localhost:2000/uploadprogress');
eventSource.onmessage = function(event) {
const data = JSON.parse(event.data);
if (data.status === 'in-progress') {
console.log(`Validation progress: ${data.progress}%`);
} else if (data.status === 'complete') {
console.log(data.message);
eventSource.close();
}
};
eventSource.onopen = function() {
console.log('Connected to the server for progress updates');
};
});
}
uploadMusicData();
Instruction
- Start the server by running
node server.js
1.1. Your terminal will display:Server running on http://localhost:2000 - Open your browser and enter:
http://localhost:2000
2.1. Your browser will display:Hello world - Open the browser console and run Client code
3.1. Your terminal will first log:Received music data: {"title":"My Awesome Track","size":1234}
3.2. Then, your browser console will display:>> Music data received and processing started >> Connected to the server for progress updates >> Validation progress: 18% >> Validation progress: 28% >> Validation progress: 39% >> Validation progress: 50% >> Validation progress: 65% >> Validation progress: 80% >> Validation progress: 97% >> Music validation complete and valid!
Publish-Subcribe #
- Also known as Message Queue Design Pattern
- Used in microservices architectures
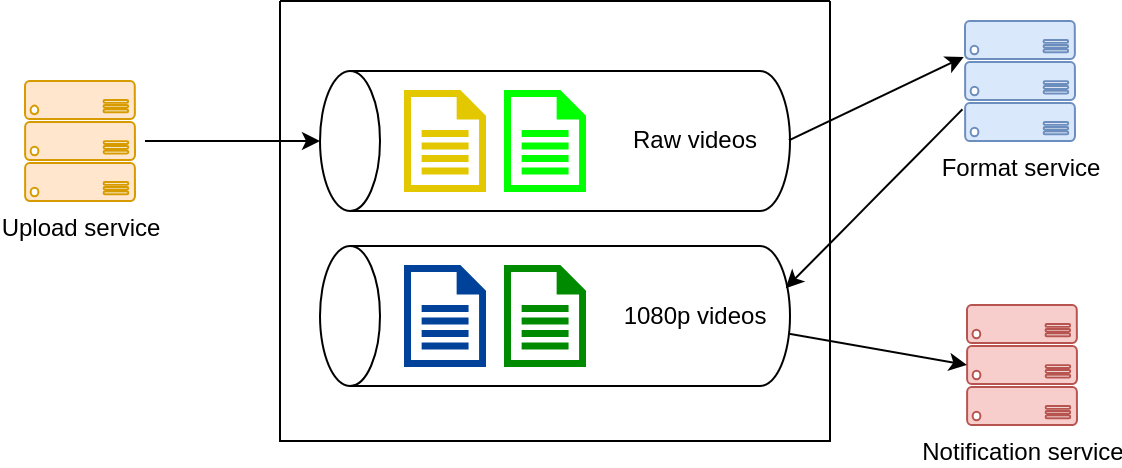
RabbitMQ #
- Producer sends and monitors if the message reaches the intended consumer
- Messages are deleted once consumed
- Designed for complex message routing
- Support message priorities
Kafka #
- Consumers keep track of message retrieval with an offset tracker
- Retain messages according to the retention policy
- There’s no message priority
Reference #
- Freecodecamp: Communication Design Patterns for Backend Development (Sep 12th, 2023)
- Udemy: Fundamentals of Backend Engineering (Feb, 2024)
- Linkedin: Understanding Short Polling: A Simple Backend Communication Pattern (Aug 7th, 2024)
- Stackoverflow: WebSockets vs. Server-Sent events/EventSource (Mar 16th, 2011)
- Amazon: Message Queues
- Amazon: What’s the Difference Between Kafka and RabbitMQ?
Help improve my blog
Was this page helpful to you?
This page was last modified at 2023-11-15