AWS Overview #
Ref: Slide #
Types of Cloud Computing #
EC2 - Elastic Compute Cloud #
- EC2 = Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- On-Demand Instances – short workload, predictable pricing, pay by second
- Has the highest cost
- Recommended for short-term and un-interrupted workloads, where you can’t predict how the application will behave
- Reserved (1 & 3 years)
- Reserved Instances – long workloads
- Recommended for steady-state usage applications (think database)
- Convertible Reserved Instances – long workloads with flexible instances
- Reserved Instances – long workloads
- Savings Plans (1 & 3 years) – commitment to an amount of usage, long workload
- Spot Instances – short workloads, cheap, can lose instances (less reliable)
- The MOST cost-efficient
- Dedicated Hosts – book an entire physical server, control instance placement
- The most expensive option
- Dedicated Instances – no other customers will share your hardware
- No control over instance placement
- Capacity Reservations – reserve capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
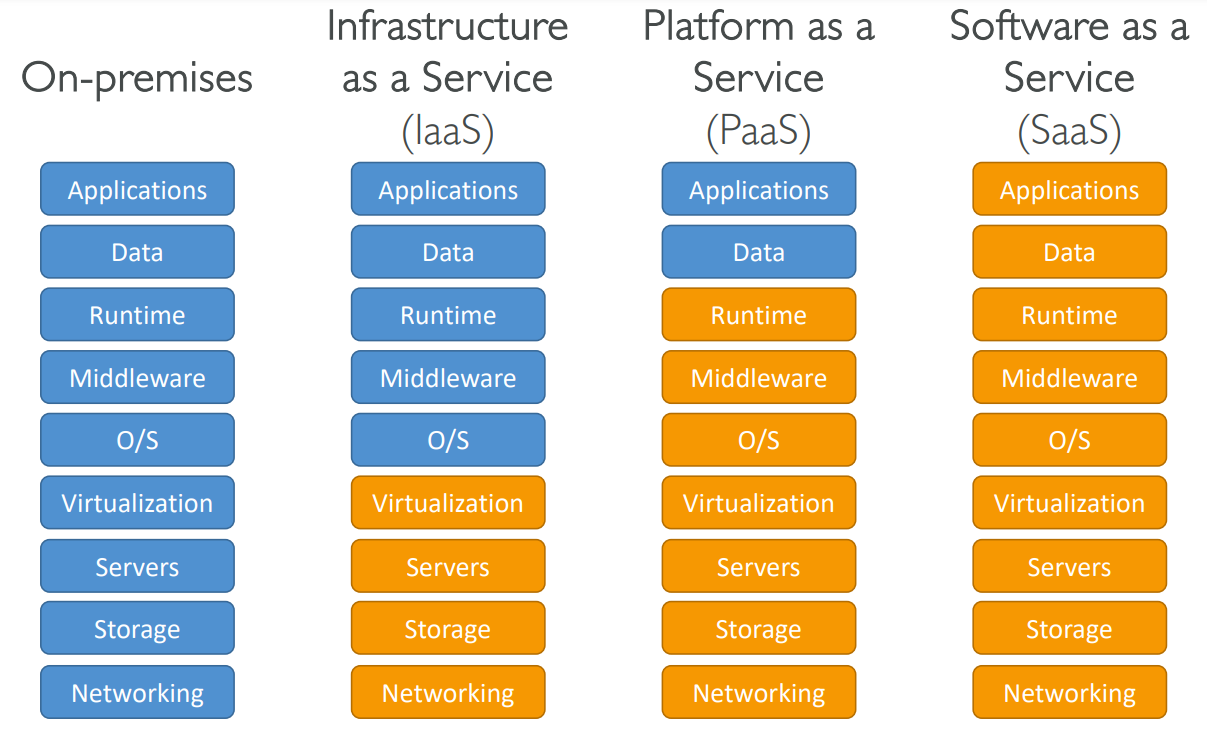
AMI - Amazon Machine Image #
- AMI are a customization of an EC2 instance
- AMI are built for a specific region (and can be copied across regions)
- You can launch EC2 instances from:
- A Public AMI: AWS provided
- Your own AMI: you make and maintain them yourself
- An AWS Marketplace AMI: an AMI someone else made (and potentially sells)
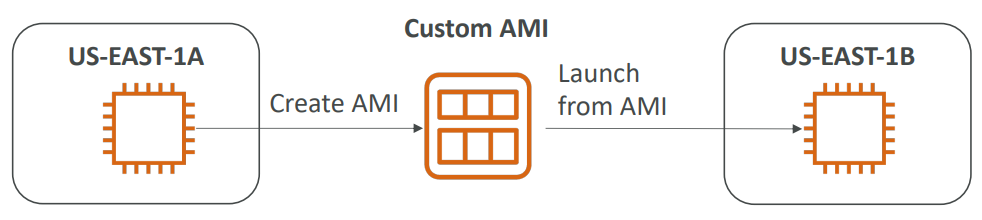
EC2 Image Builder #
- Used to automate the creation of Virtual Machines or container images
=> Automate the creation, maintain, validate and test EC2 AMIs - Can be run on a schedule (weekly, whenever packages are updated, etc…)
- Free service (only pay for the underlying resources)
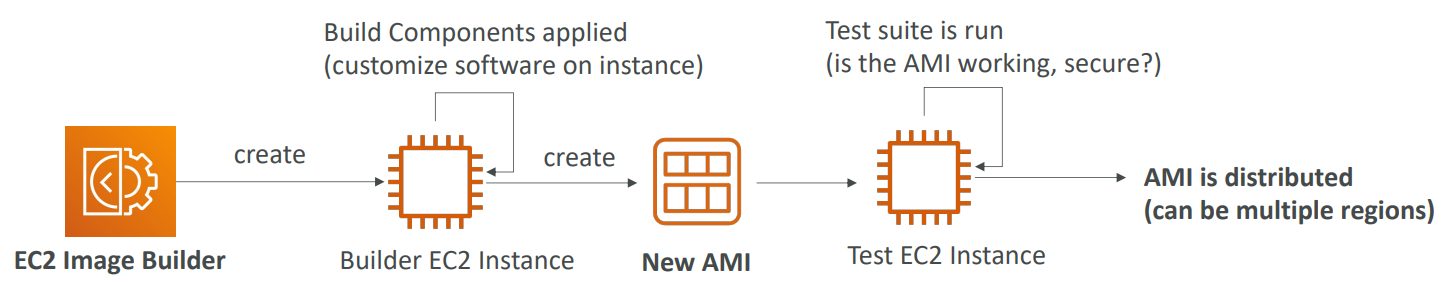
EBS - Elastic Block Store #
- A network drive you can attach to your instances while they run
- It allows your instances to persist data, even after their termination
- They can only be mounted to one instance at a time
- They are bound to a specific AZ
Think of them as a “network USB stick”
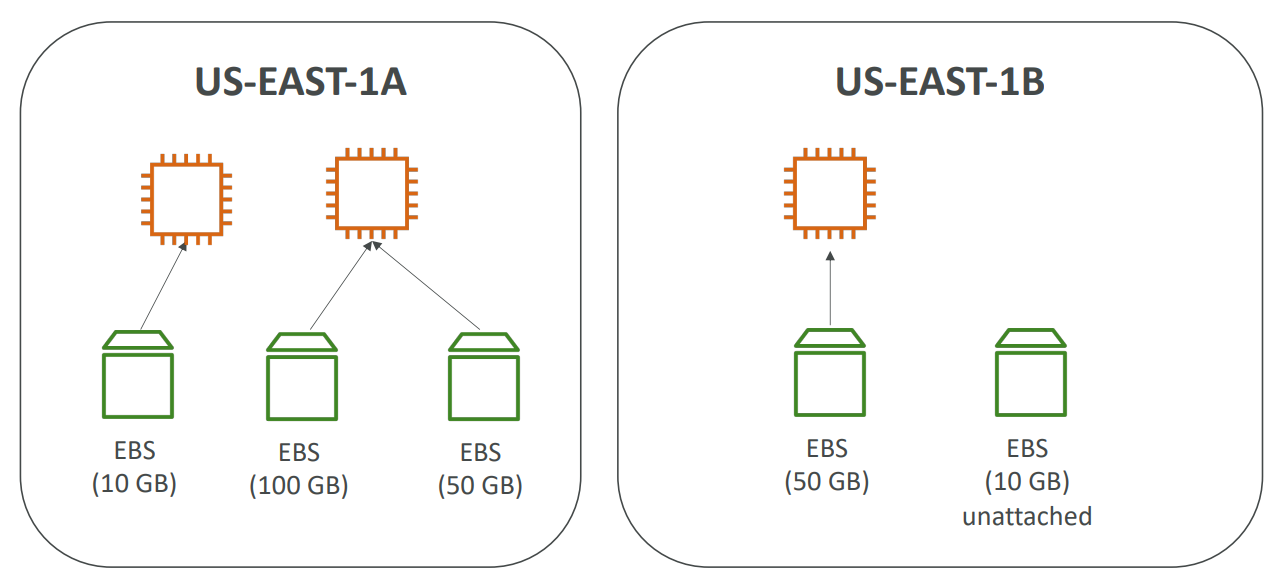
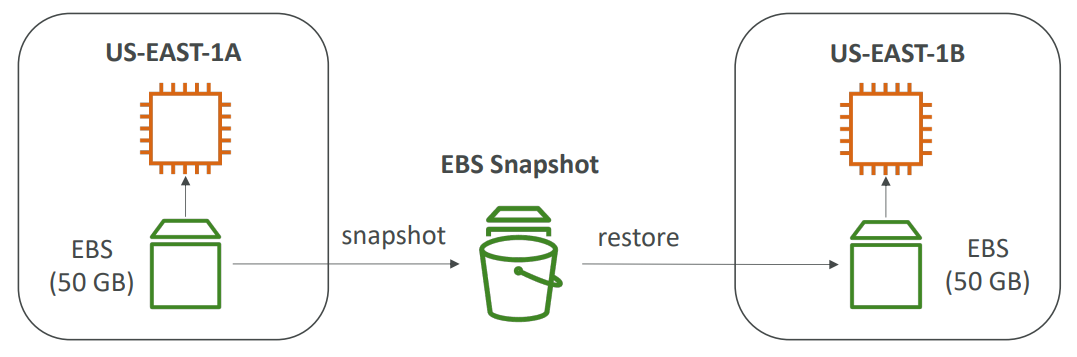
Snapshots #
- Make a backup (snapshot) of your EBS volume at a point in time
- Can copy snapshots across AZ or Region
Snapshots Features #
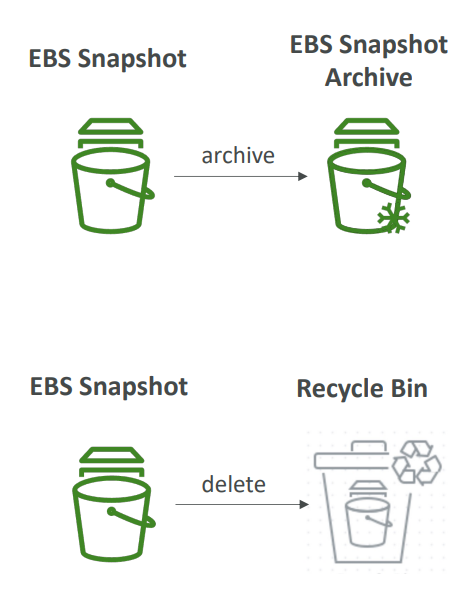
- Snapshot Archive
- Move a Snapshot to an ”archive tier” that is 75% cheaper
- Takes within 24 to 72 hours for restoring the archive
- Recycle Bin for EBS Snapshots
- Setup rules to retain deleted snapshots so you can recover them after an accidental deletion
- Specify retention (from 1 day to 1 year)
EC2 Instance Store #
- If you need a high-performance hardware disk, use EC2 Instance Store
- Better I/O performance
- EC2 Instance Store lose their storage if they’re stopped (ephemeral)
- Good for buffer / cache / scratch data / temporary content
- Risk of data loss if hardware fails
- Backups and Replication are your responsibility
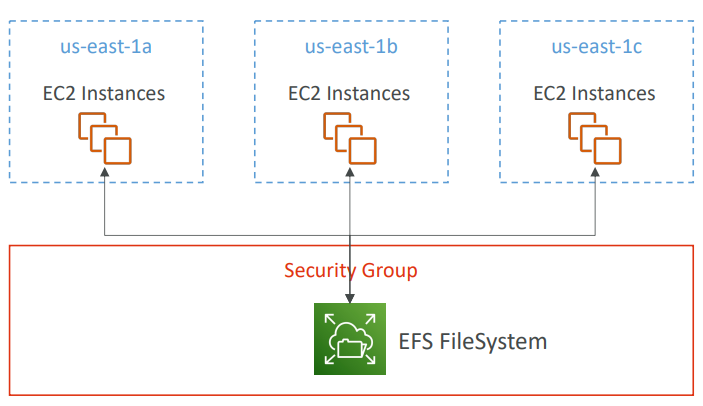
EFS - Elastic File System #
- Managed NFS (network file system) that can be mounted on 100s of EC2
- EFS works with Linux EC2 instances in multi-AZ
- Highly available, scalable, expensive (3x gp2), pay per use, no capacity planning
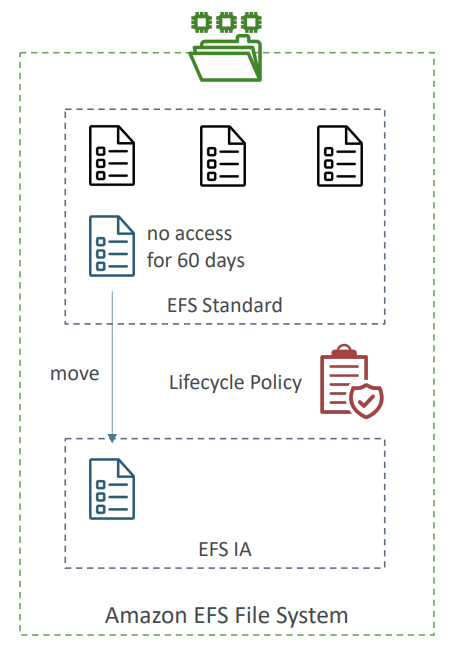
EFS IA - EFS Infrequent Access #
- Storage class that is cost-optimized for files not accessed every day
- EFS will automatically move your files to EFS-IA based on the last time they were accessed
- Enable EFS-IA with a Lifecycle Policy
FSx #
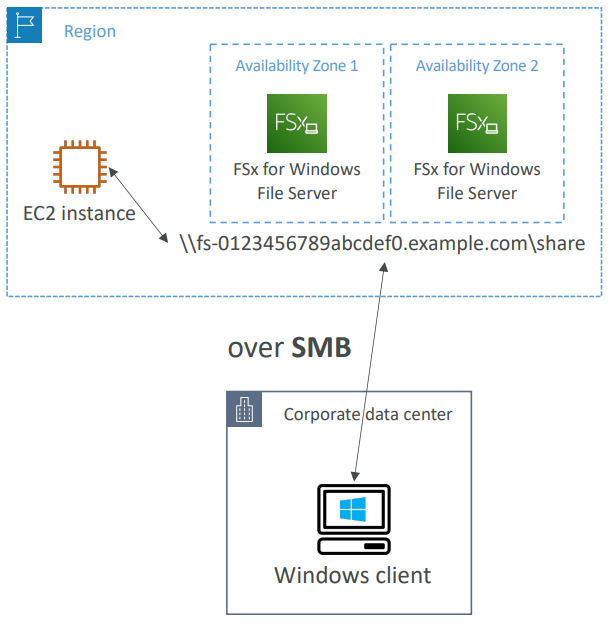
for Windows File Server #
- A fully managed, highly reliable, and scalable Windows native shared file system
- Built on Windows File Server
- Supports SMB protocol & Windows NTFS
- Integrated with Microsoft Active Directory
- Can be accessed from AWS or your on-premise infrastructure
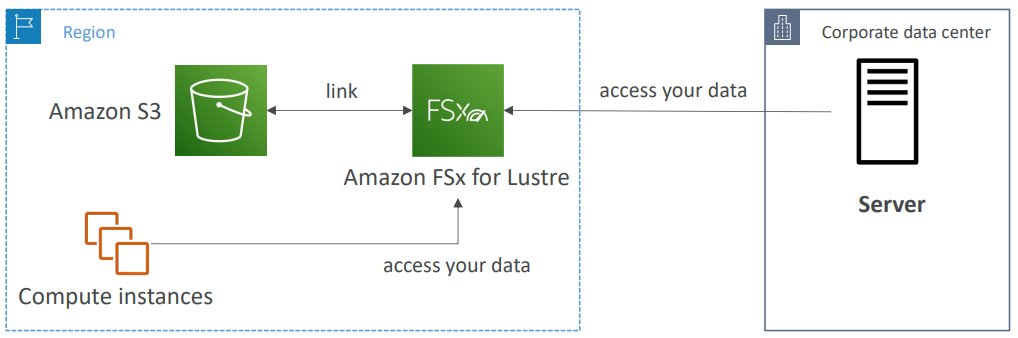
for Lustre #
- A fully managed, high-performance, scalable file storage for High Performance Computing (HPC)
- The name Lustre is derived from “Linux” and “cluster”
- Machine Learning, Analytics, Video Processing, Financial Modeling, …
S3 #
- “infinitely scaling” storage
Buckets #
- Allows people to store objects (files) in buckets (directories)
- Buckets must have a globally unique name (across all regions all accounts)
- Buckets are defined at the region level
- Naming convention
- No uppercase, No underscore
- 3-63 characters long
- Not an IP
- Must start with lowercase letter or number
- Must NOT start with the prefix xn–
- Must NOT end with the suffix -s3alias
Objects #
- Objects (files) have a Key
- The key is the FULL path:
- s3://my-bucket/my_file.txt
- s3://my-bucket/my_folder1/another_folder/my_file.txt
- The key is composed of prefix + object name
- s3://my-bucket/my_folder1/another_folder/my_file.txt
- There’s no concept of “directories” within buckets
(although the UI will trick you to think otherwise) - Just keys with very long names that contain slashes (“/”)
- Object values are the content of the body:
- Max. Object Size is 5TB (5000GB)
- If uploading more than 5GB, must use “multi-part upload”
Security #
- User-Based
- IAM Policies – which API calls should be allowed for a specific user from IAM
- Resource-Based
- Bucket Policies – bucket wide rules from the S3 console - allows cross account
- Object Access Control List (ACL) – finer grain (can be disabled)
- Bucket Access Control List (ACL) – less common (can be disabled)
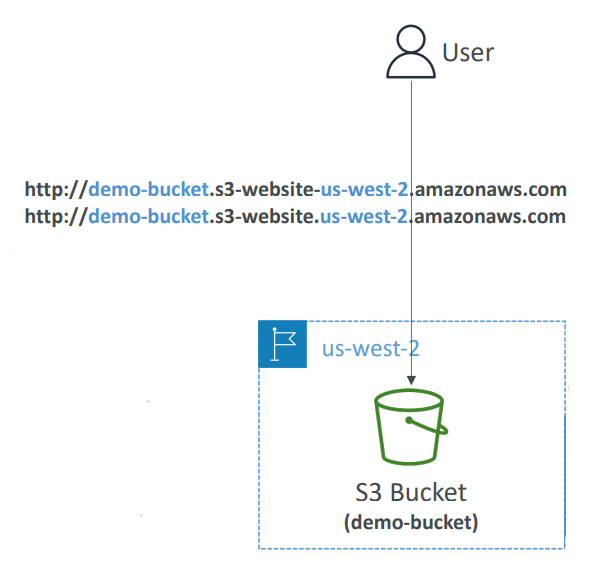
Static Website Hosting #
- S3 can host static websites and have them accessible on the Internet
- The website URL will be (depending on the region)
- http
://
bucket-name
.s3-website-aws-region.amazonaws.com
OR - http :// bucket-name .s3-website.aws-region.amazonaws.com
- http
://
bucket-name
.s3-website-aws-region.amazonaws.com
- If you get a 403 Forbidden error, make sure the bucket policy allows public reads!
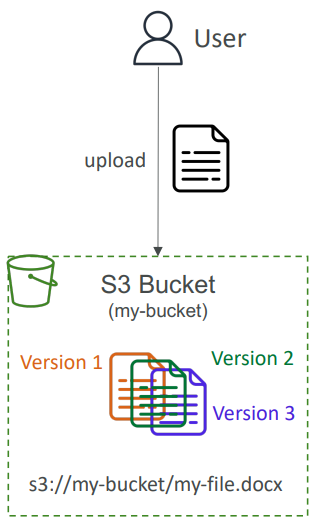
Versioning #
- It is enabled at the bucket level
- It is best practice to version your buckets
- Protect against unintended deletes (ability to restore a version)
- Easy roll back to previous version
- Notes:
- Any file that is not versioned prior to enabling versioning will have version “null”
- Suspending versioning does not delete the previous versions
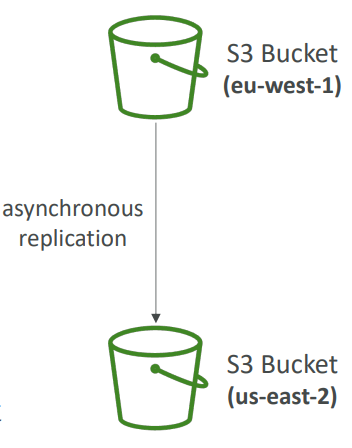
Replication #
- Must enable Versioning in source and destination buckets
- Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
- Same-Region Replication (SRR)
- Buckets can be in different AWS accounts
- Copying is asynchronous
- Must give proper IAM permissions to S3
- Use cases:
- CRR – compliance, lower latency access, replication across accounts
- SRR – log aggregation, live replication between production and test accounts
Storage Classes #
- Amazon S3 Standard - General Purpose
- Used for frequently accessed data
- Use Cases: Big Data analytics, mobile & gaming applications, content distribution
- Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (IA)
- For data that is less frequently accessed, but requires rapid access when needed
- Use cases: Disaster Recovery, backups
- Amazon S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access
- For data that is less frequently accessed, but requires rapid access when needed
- In a single AZ; data lost when AZ is destroyed
- Use Cases: Storing secondary backup copies of on-premise data, or data you can recreate
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
- For data accessed once a quarter
- Millisecond retrieval
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval (formerly Amazon S3 Glacier)
- Retrieval: Expedited (1 to 5 minutes), Standard (3 to 5 hours), Bulk (5 to 12 hours) – free
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive
- For long term storage
- Retrieval: Standard (12 hours), Bulk (48 hours)
- Amazon S3 Intelligent Tiering
Moves objects automatically between Access Tiers based on usage- Frequent Access tier (automatic): default tier
- Infrequent Access tier (automatic): objects not accessed for 30 days
- Archive Instant Access tier (automatic): objects not accessed for 90 days
- Archive Access tier (optional): configurable from 90 days to 700+ days
- Deep Archive Access tier (optional): config. from 180 days to 700+ days
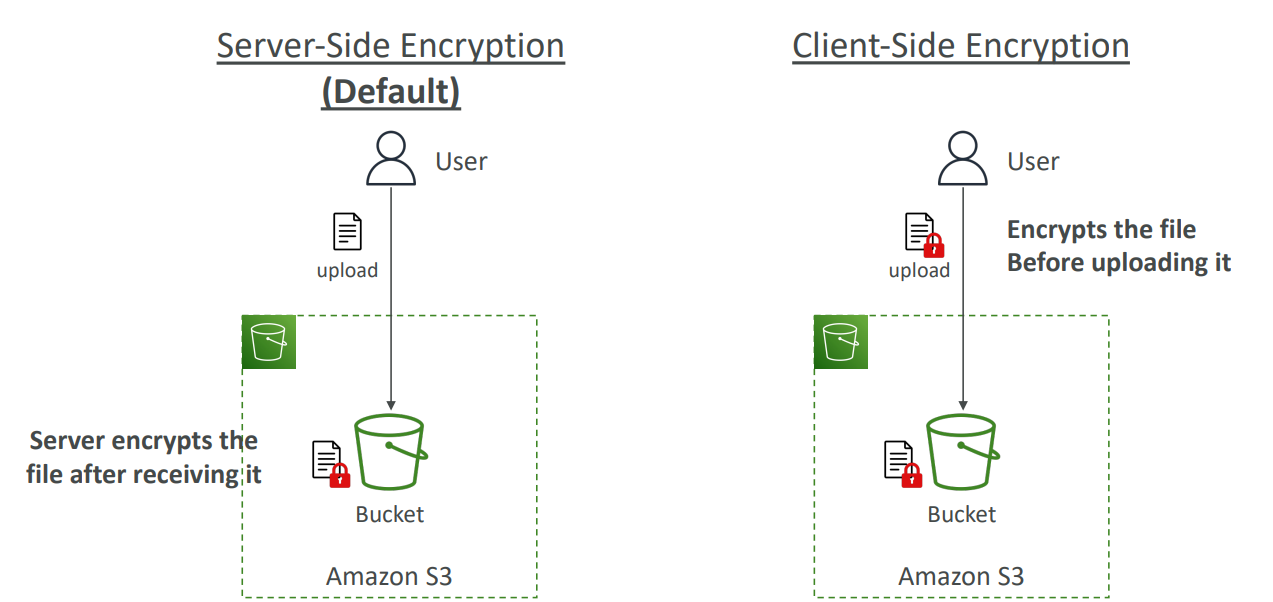
Encryption #
IAM Access Analyzer #
- Ensures that only intended people have access to your S3 buckets
- Example: publicly accessible bucket, bucket shared with other AWS account…
- Evaluates S3 Bucket Policies, S3 ACLs, S3 Access Point Policies
- Powered by IAM Access Analyzer
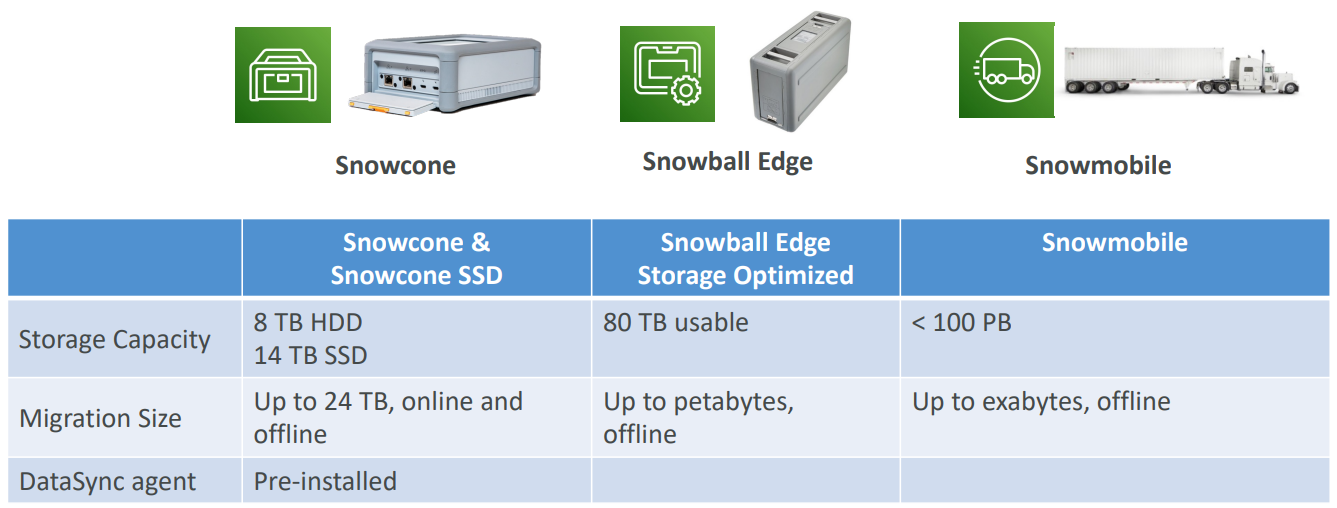
Snow Family #
- Highly-secure, portable devices to collect and process data at the edge, and migrate data into and out of AWS
- Data migration: Snowcone, Snowball Edge, Snowmobile
- Edge computing: Snowcone, Snowball Edge
OpsHub #
- A software you install on your computer / laptop
- To manage your Snow Family Device
- Transferring files
- Launch compatible AWS services on your devices (ex: Amazon EC2 instances, AWS DataSync, Network File System (NFS))
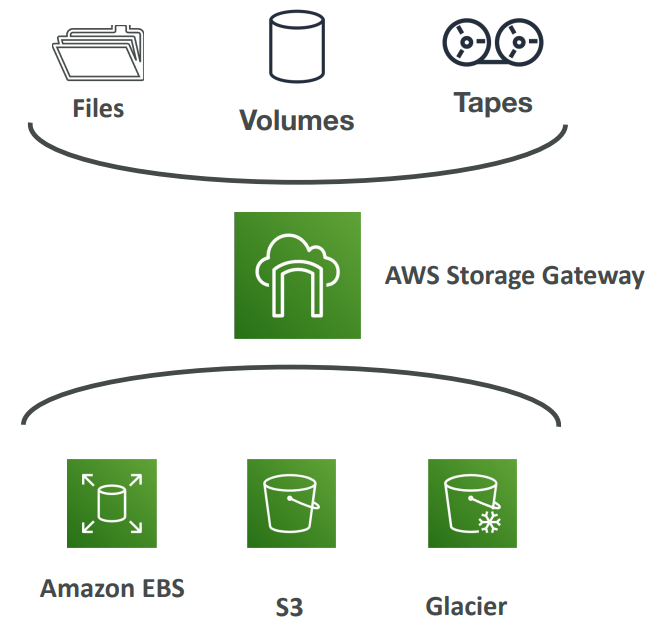
Storage Gateway #
- Bridge between on-premise data and cloud data in S3
- Hybrid storage service to allow on-premises to seamlessly use the AWS Cloud
- Use cases: disaster recovery, backup & restore, tiered storage
Monitoring #
- CloudWatch:
- Metrics: monitor the performance of AWS services and billing metrics
- Alarms: automate notification, perform EC2 action, notify to SNS based on metric
- Logs: collect log files from EC2 instances, servers, Lambda functions…
- Events (or EventBridge): react to events in AWS, or trigger a rule on a schedule
- CloudTrail: audit API calls made within your AWS account
- CloudTrail Insights: automated analysis of your CloudTrail Events
- X-Ray: trace requests made through your distributed applications
- AWS Health Dashboard: status of all AWS services across all regions
- AWS Account Health Dashboard: AWS events that impact your infrastructure
- Amazon CodeGuru: automated code reviews and application performance recommendations
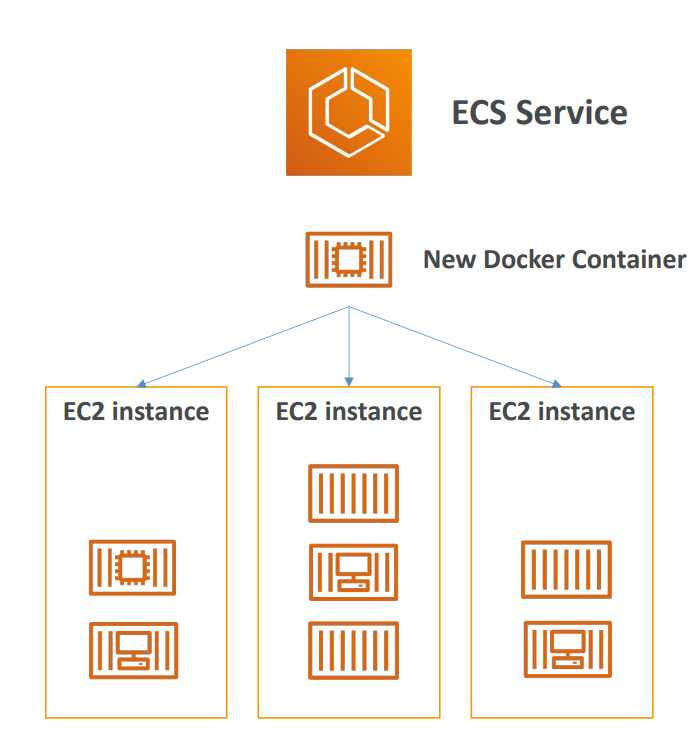
ECS - Elastic Container Service #
- You must provision & maintain the infrastructure (the EC2 instances)
Fargate #
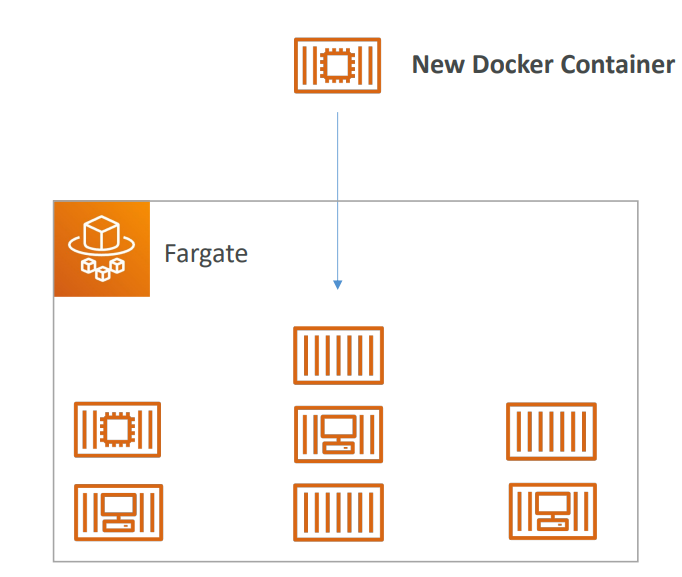
- You do not provision the infrastructure (no EC2 instances to manage) – simpler!
- Serverless offering
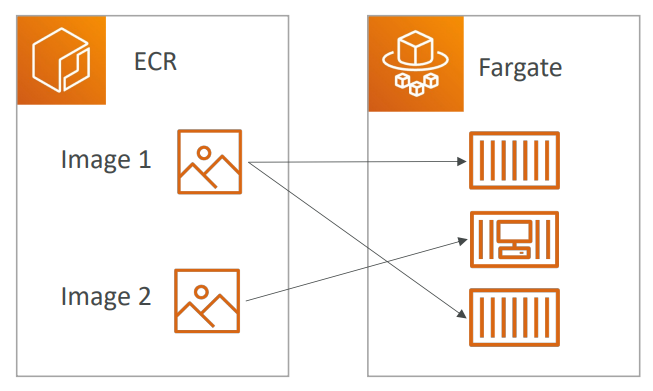
ECR - Elastic Container Registry #
- Store your Docker images
Lambda #
- Virtual functions – no servers to manage!
- Limited by time - short executions
- Run on-demand
- Scaling is automated!
- Event-Driven: functions get invoked by AWS when needed
Pricing #
- Pay per calls
- Pay per duration
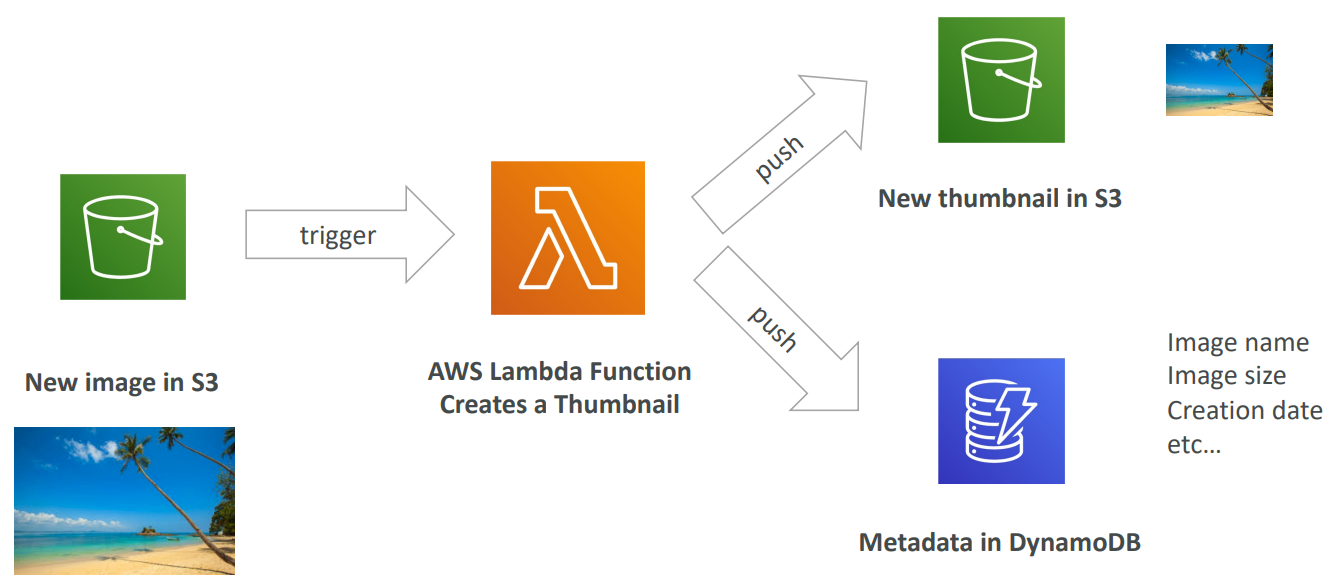
Example #
Serverless Thumbnail creation
Serverless CRON Job
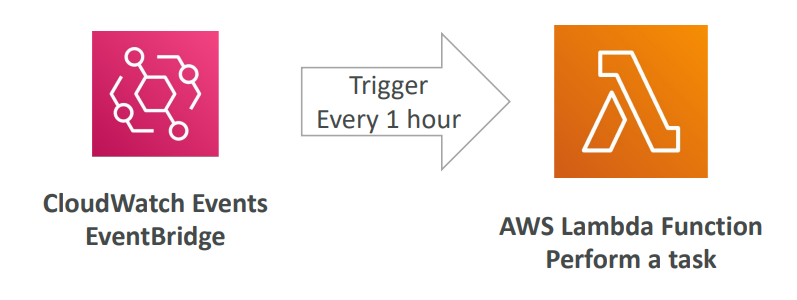
API Gateway #
- Serverless and scalable
- Supports RESTful APIs and WebSocket APIs
- Support for security, user authentication, API throttling, API keys, monitoring…
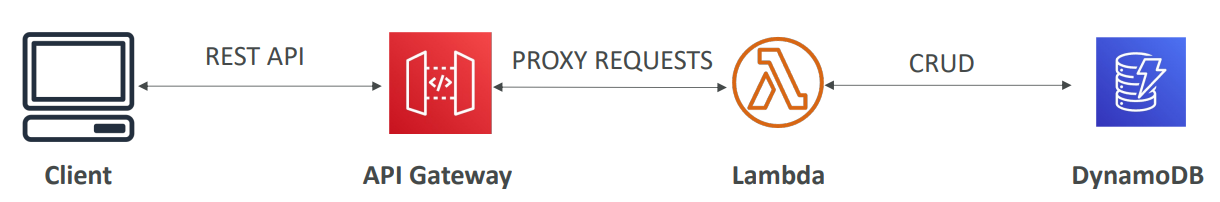
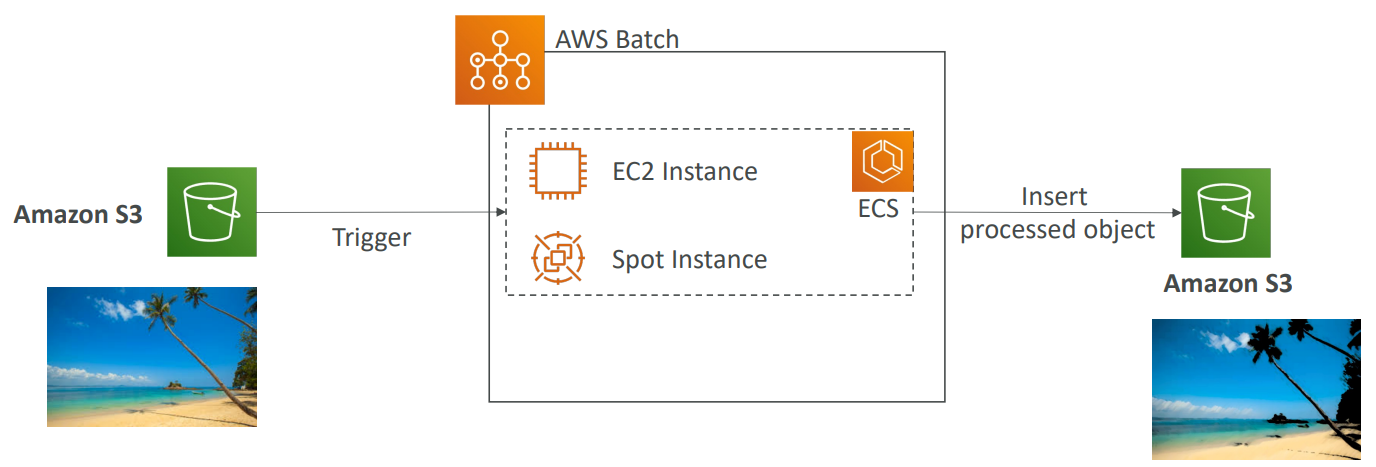
Batch #
- Fully managed batch processing at any scale
- Batch will dynamically launch EC2 instances or Spot Instances
- Batch jobs are defined as Docker images and run on ECS
Batch vs Lambda #
Lambda
- Time limit
- Limited runtimes
- Limited temporary disk space
- Serverless
Batch
- No time limit
- Any runtime as long as it’s packaged as a Docker image
- Rely on EBS / instance store for disk space
- Relies on EC2 (can be managed by AWS)
Lightsail #
- Simpler alternative to using EC2, RDS, ELB, EBS, Route 53
- Great for people with little cloud experience!
- “almost always be a wrong answer”
CloudFormation #
Infrastructure as code
Within a CloudFormation template, you say:
- I want a security group
- I want two EC2 instances using this security group
- I want an S3 bucket
- I want a load balancer (ELB) in front of these machines
Then CloudFormation creates those for you, in the right order, with the exact configuration that you specify
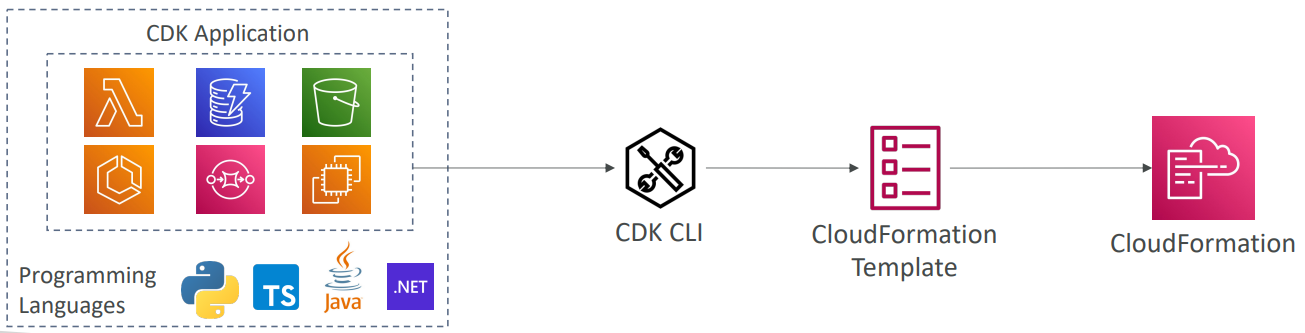
CDK - Cloud Development Kit #
- Define your cloud infrastructure using a familiar language: JavaScript, Python, …
- You can use
forloop to create multiple instances
- You can use
- The code is “compiled” into a CloudFormation template (JSON/YAML)
- You can therefore deploy infrastructure and application runtime code together
Elastic Beanstalk #
Overview #
- A developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
- It uses all the component’s we’ve seen before: EC2, ASG, ELB, RDS, etc
- Beanstalk = Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Beanstalk is free but you pay for the underlying instances
- Just the application code is the responsibility of the developer
- Three architecture models:
- Single Instance deployment: good for dev
- LB + ASG: great for production or pre-production web applications
- ASG only: great for non-web apps in production (workers, etc..)
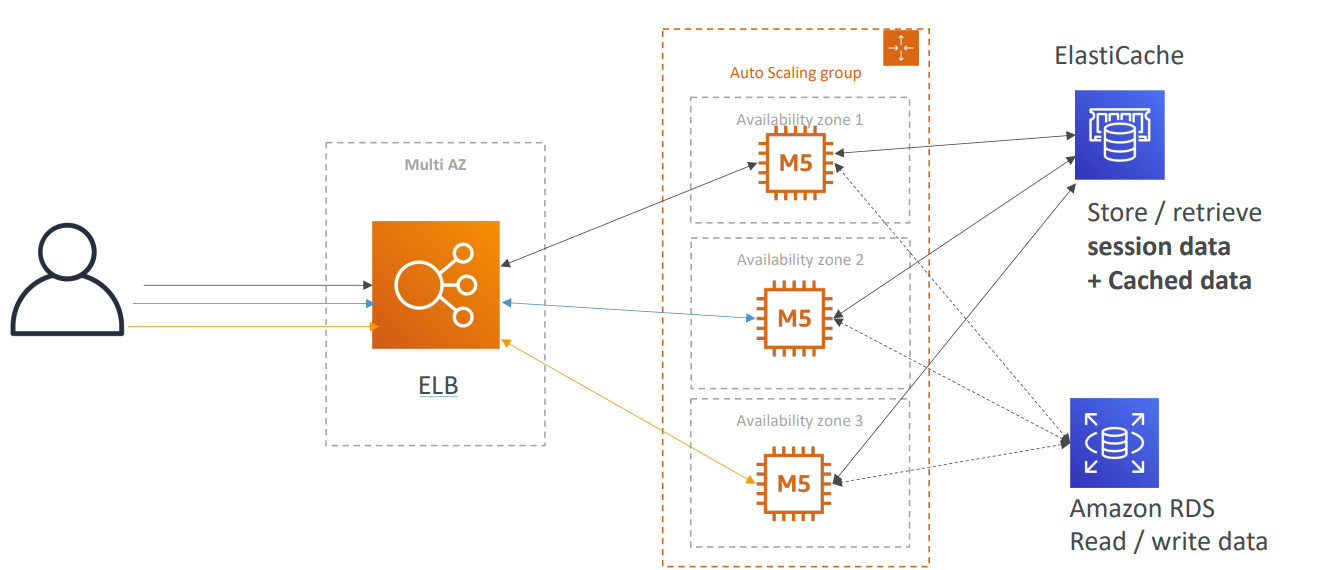
Health Monitoring #
- Health agent pushes metrics to CloudWatch
- Checks for app health, publishes health events
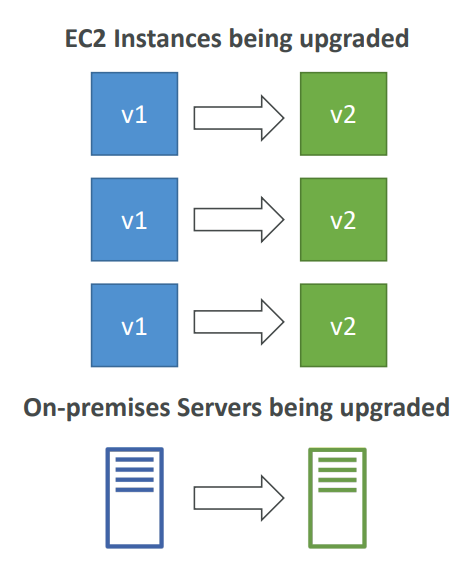
CodeDeploy #
- We want to deploy our application automatically
- Works with EC2 Instances
- Works with On-Premises Servers
- Hybrid service
- Servers / Instances must be provisioned and configured ahead of time with the CodeDeploy Agent
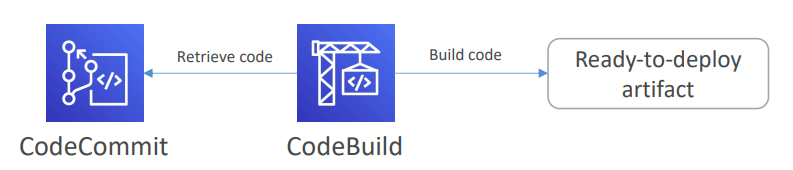
CodeCommit #
- Like GitHub
- Developers usually store code in a repository, using the Git technology
CodeBuild #
- Compiles source code, run tests, and produces packages that are ready to be deployed (by CodeDeploy for example)
- Pay-as-you-go pricing - only pay for the build time
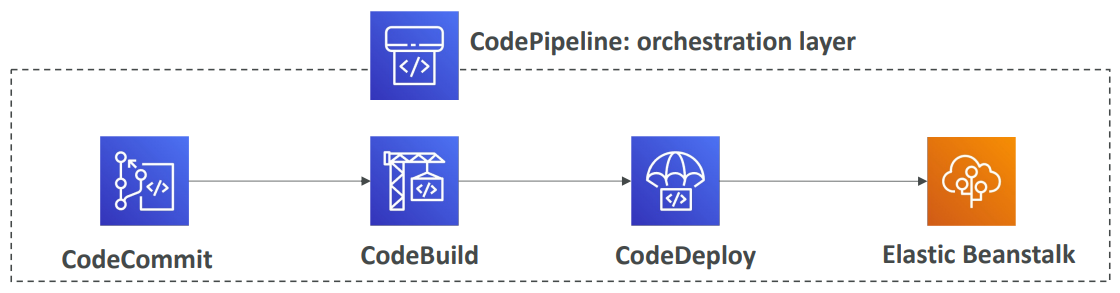
CodePipeline #
- Orchestrate the different steps to have the code automatically pushed to production
- Code => Build => Test => Provision => Deploy
- Basis for CICD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery)
CodeArtifact #
- Software packages depend on each other to be built (also called code dependencies), and new ones are created
- Storing and retrieving these dependencies is called artifact management
- Developers and CodeBuild can then retrieve dependencies straight from CodeArtifact
CodeStar #
- Unified UI
- Set-up CodeCommit, CodePipeline, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, EC2, etc
Cloud9 #
- A cloud IDE
- Allows for code collaboration in real-time (pair programming)
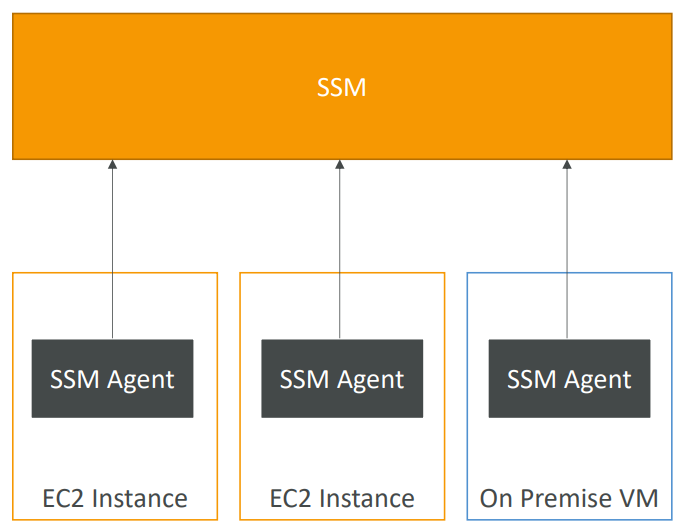
SSM - Systems Manager #
- Manage your EC2 and On-Premises
- Hybrid AWS service
Session Manager #
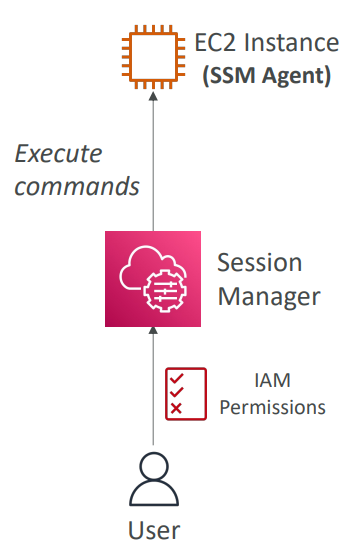
- Allows you to start a secure shell on your EC2 and on-premises servers
- No SSH access, bastion hosts, or SSH keys needed
- No port 22 needed (better security)
- Supports Linux, macOS, and Windows
- Send session log data to S3 or CloudWatch Logs
Parameter Store #
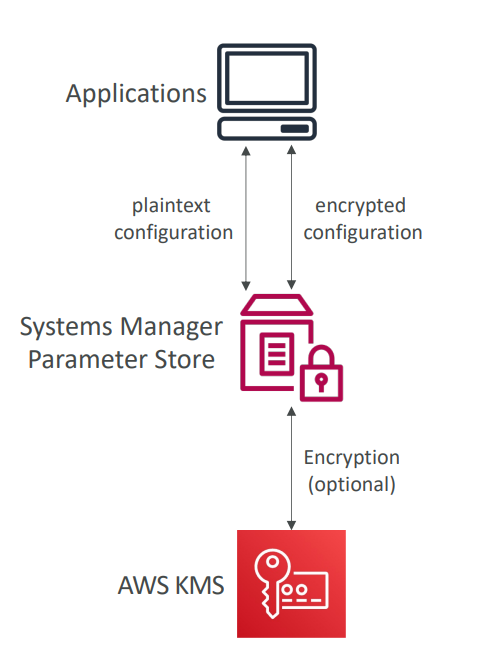
- Secure storage for configuration and secrets
- API Keys, passwords, configurations…
- Serverless, scalable, durable, easy SDK
- Control access permissions using IAM
- Version tracking & encryption (optional)
OpsWorks #
- AWS OpsWorks = Managed Chef & Puppet
- Chef & Puppet (2 tools not created by AWS) help you perform server configuration automatically, or repetitive actions
Route 53 - DNS #
- Route53 is a Managed DNS (Domain Name System)
- DNS is a collection of rules and records which helps clients understand how to reach a server through URLs
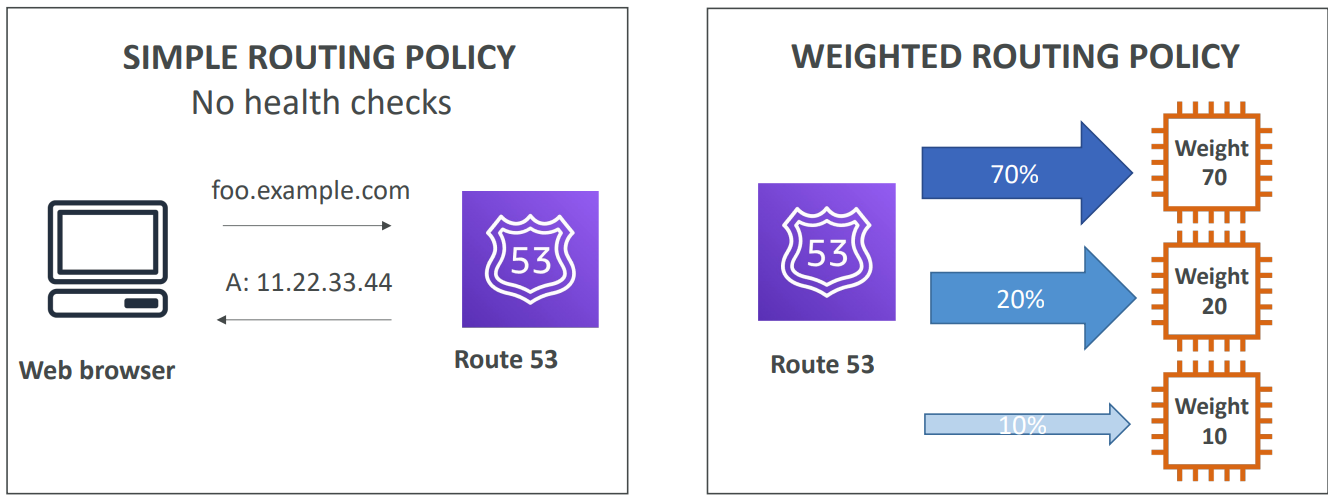
Routing Policies #
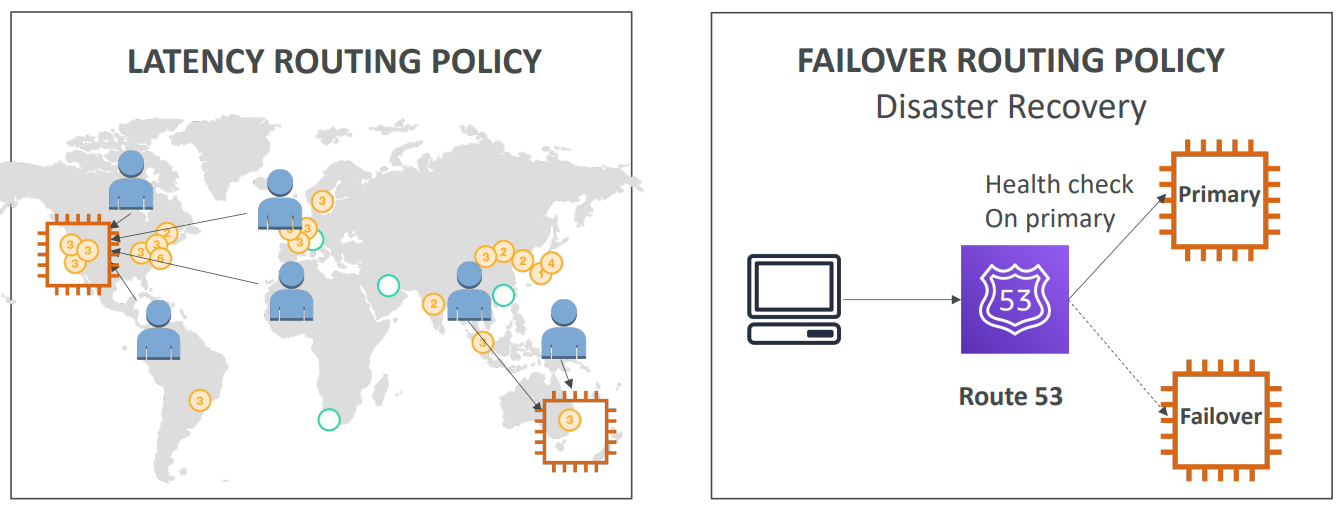
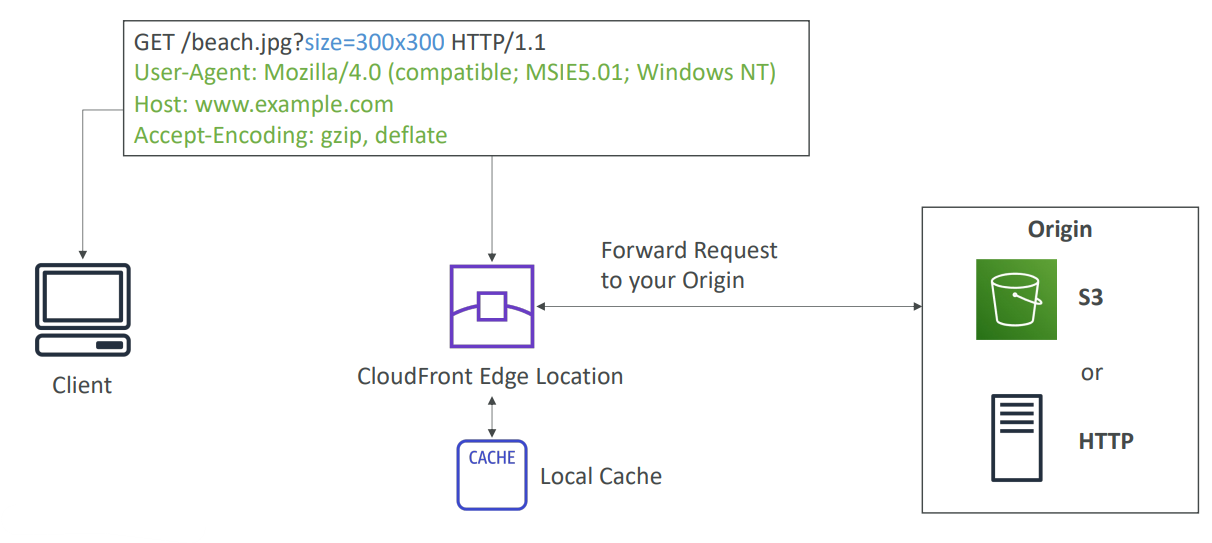
CloudFront - CDN #
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Improves read performance, content is cached at the edge
- DDoS protection (because worldwide), integration with Shield, AWS Web Application Firewall
- S3 bucket
- Enhanced security with CloudFront Origin Access Control (OAC)
- OAC is replacing Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- CloudFront can be used as an ingress (to upload files to S3)
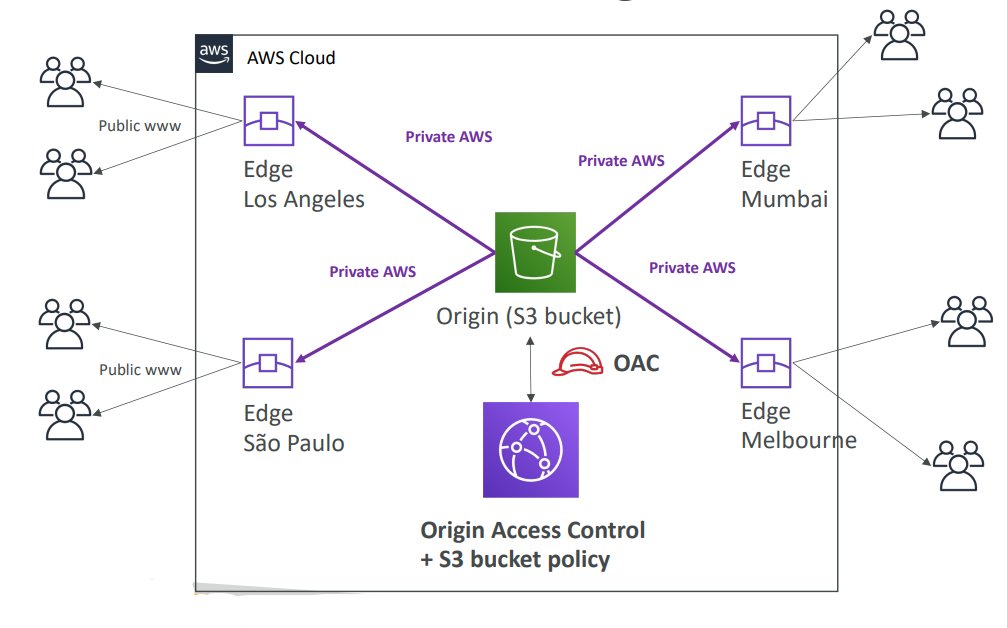
CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication #
CloudFront: #
- Global Edge network
- Files are cached for a TTL (maybe a day)
- Great for static content that must be available everywhere
S3 Cross Region Replication: #
- Must be setup for each region you want replication to happen
- Files are updated in near real-time
- Read only
- Great for dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in few regions
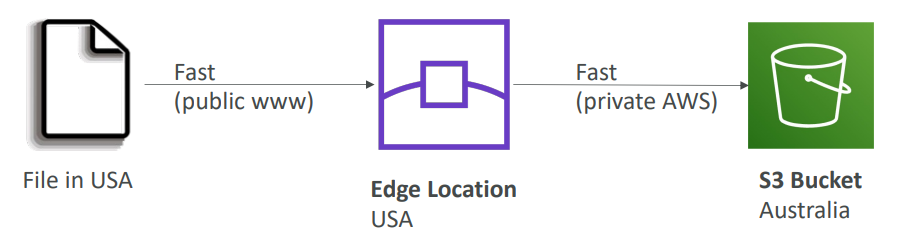
S3 Transfer Acceleration #
- Increase transfer speed by transferring file to an AWS edge location which will forward the data to the S3 bucket in the target region
Global Accelerator #
- Improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network
- Leverage the AWS internal network to optimize the route to your application (60% improvement)
- 2 Anycast IP are created for your application and traffic is sent through Edge Locations
- The Edge locations send the traffic to your application
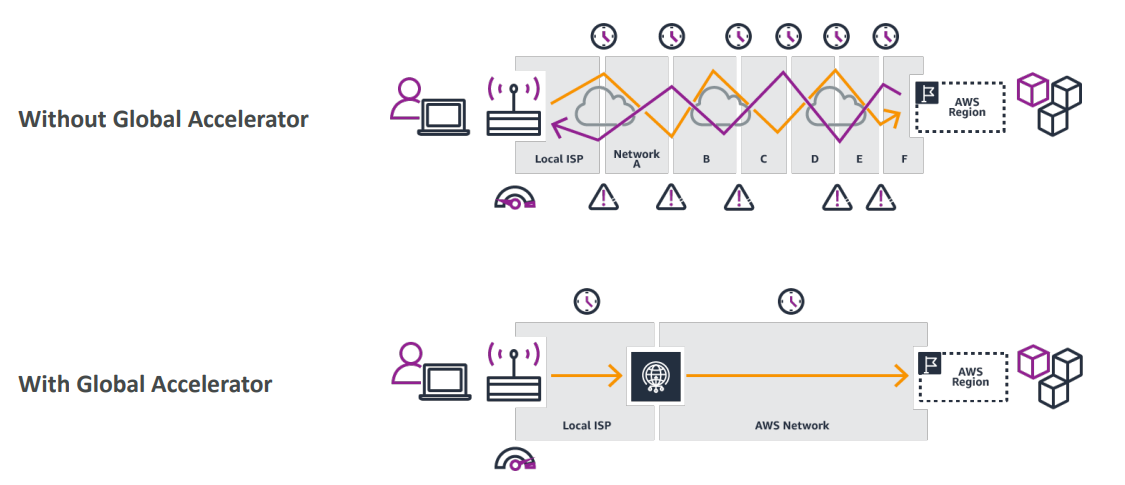
AWS Global Accelerator vs CloudFront #
- They both use the AWS global network and its edge locations around the world
- Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection
CloudFront - CDN #
- Improves performance for your cacheable content (such as images and videos)
- Content is served at the edge
Global Accelerator #
- No caching, proxying packets at the edge to applications running in one or more AWS Regions.
- Improves performance for a wide range of applications over TCP or UDP
- Good for HTTP use cases that require static IP addresses
- Good for HTTP use cases that required deterministic, fast regional failover
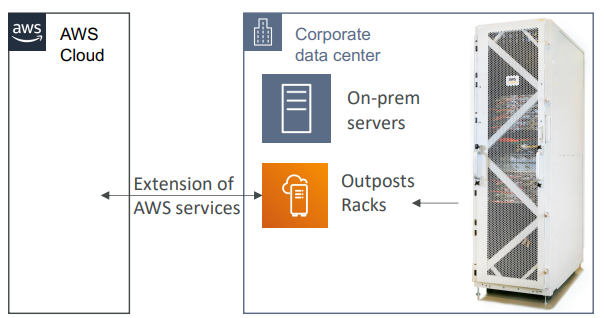
Outposts #
- Hybrid Cloud: businesses that keep an on-premises infrastructure alongside a cloud infrastructure
- AWS Outposts are “server racks” that offers the same AWS infrastructure, services, APIs & tools to build your own applications on-premises just as in the cloud
- AWS will setup and manage “Outposts Racks” within your on-premises infrastructure and you can start leveraging AWS services on-premises
- You are responsible for the Outposts Rack physical security
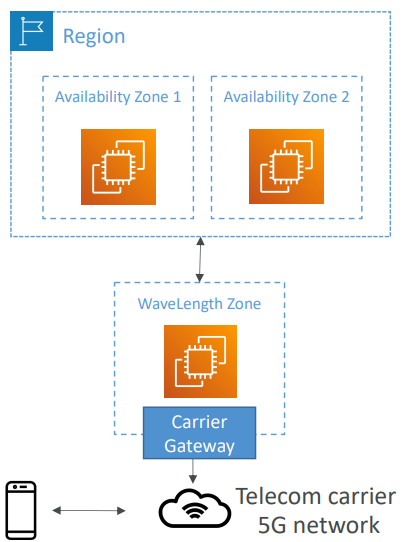
WaveLength #
- WaveLength Zones are infrastructure deployments embedded within the telecommunications providers’ datacenters at the edge of the 5G networks
- Use cases: Smart Cities, ML-assisted diagnostics, Connected Vehicles, Interactive Live Video Streams, AR/VR, Real-time Gaming, …
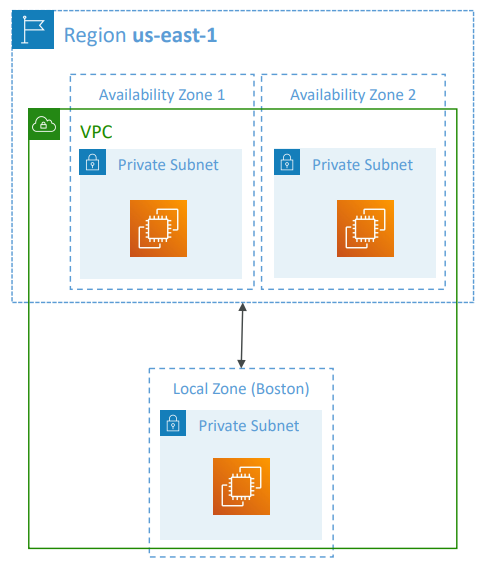
Local Zones #
- Places AWS compute, storage, database, and other selected AWS services closer to end users to run latency-sensitive applications
- Extend your VPC to more locations – “Extension of an AWS Region”
- Example:
- AWS Region: N. Virginia (us-east-1)
- AWS Local Zones: Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Miami, …
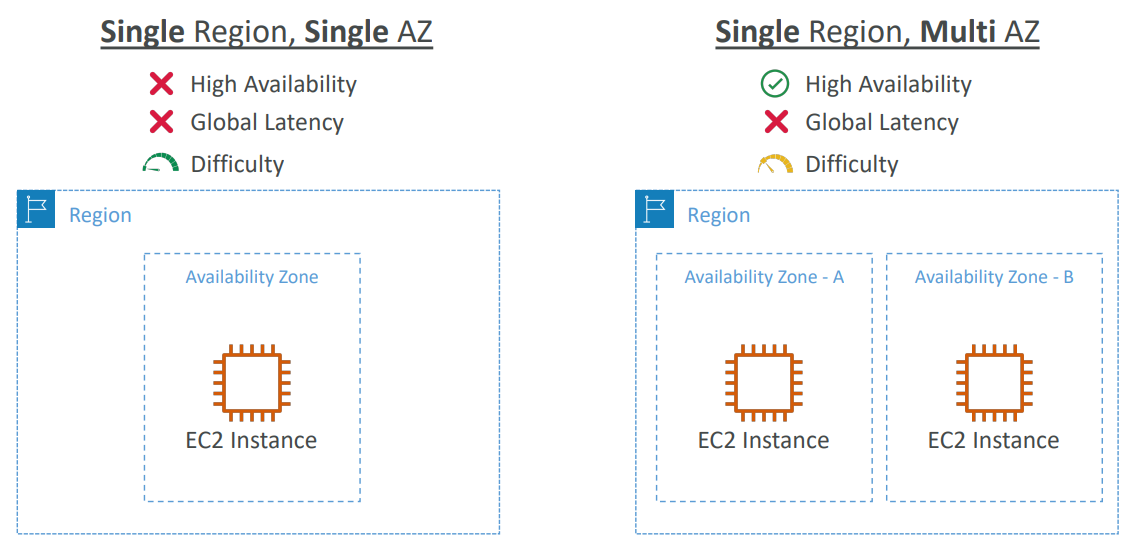
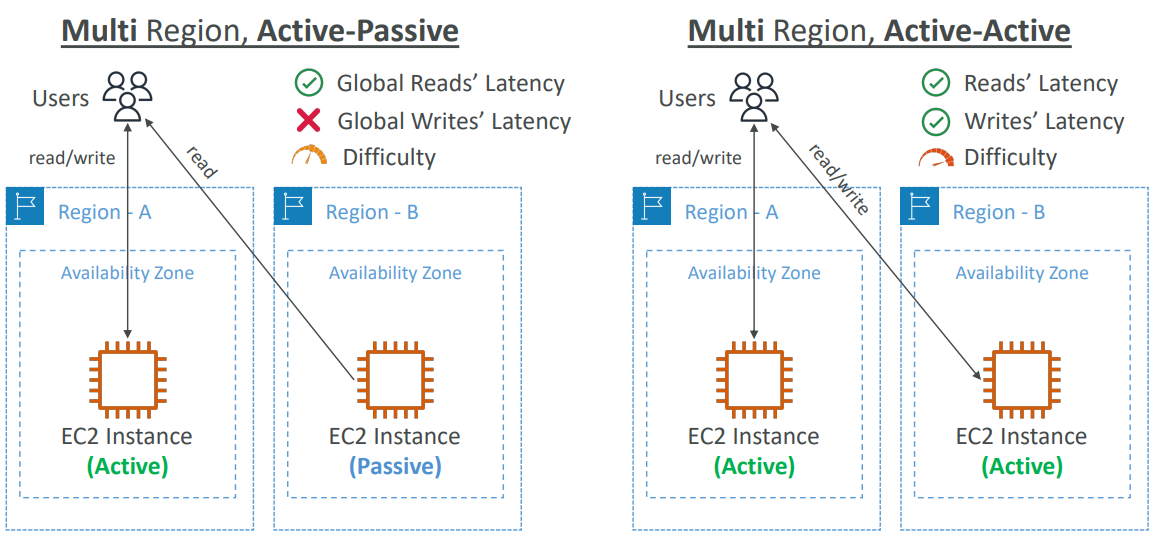
Global Applications Architecture #
Help improve my blog
Was this page helpful to you?
This page was last modified at 2023-11-15